Digital Forensics is a branch of forensic science that focuses on identifying, recovering, processing, analyzing, and reporting electronically stored data.
Electronic evidence is part of almost every criminal investigation, and digital forensic support is critical to law enforcement investigations. Electronic evidence can be collected from a variety of sources, including computers, smartphones, external storage devices, unmanned aerial systems, shipborne devices, and more.
The main goal of digital forensics is to extract data from electronic sources, convert it into useful information and present the results. All procedures use good forensic techniques to ensure the finding are admissible to the court.
Digital forensics is the preservation, identification, retrieval, and documentation of computer evidence that can use in a court of law. It is a science that looks for evidence in digital media such as computers, mobile phones, servers, and the Internet. We provide forensic teams with the best technology and tools to solve complex digital cases.
Digital Forensics History
The following are important milestones in the history of digital forensic.
Hans Gross (1847–1915): For the first time, a scientific was used to guide criminal investigations
FBI (1932): Established a laboratory to provide forensic services to all field agents and other law authorities across the USA.
In 1978 the Florida Computer Crime Act recognized the first computer crime.
Francis Golton (1911–1982): Performed the first recorded study of fingerprints.
In 1992, the term computer forensics was used in the academic literature.
The International Organization on Computer Evidence (IOCE) establish in 1995.
In 2000, the first FBI regional computer forensics lab was founded.
The Scientific Working Group on Digital Evidence (SWGDE) published the first digital forensics book “Best Practices for Computer Forensics” in 2002.
In 2010, Simson Garfinkel discovered a problem with digital research.
What Does a Digital Forensics Specialist Do?
Digital forensics professionals play an important role in investigating cybercrime. It mainly deals with the recovery of encrypted, deleted, or hidden data. Liability includes ensuring the integrity of the information that is to be used in court. Computer forensic experts can analyze by interviewing suspects, victims, and witnesses at various stages of the investigation. They also help prepare evidence for presentation in court. Private companies also work closely with digital forensics experts. Their expertise is also required in personal and network security, the defense sector, major financial institutions, and I.T. companies.
Digital Forensic Process
Digital forensics involves the following steps:
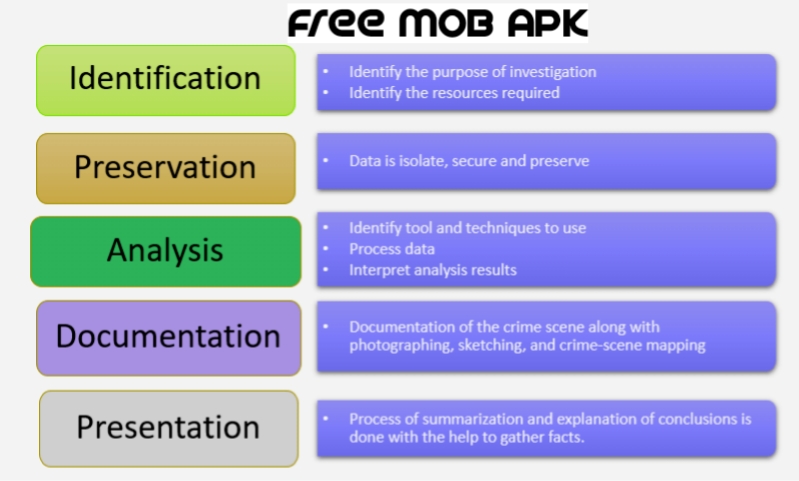
- Identification
- Preservation
- Analysis
- Documentation
- Presentation
Let’s study each in detail
Identification
The forensic procedure begins with this. The forensic process mainly involves, what proof is, where it is stored, and finally, how (in which form) it is stored.
Preservation
At this level, the data is isolated, secured, and preserved. This includes preventing people from using a digital device so the digital evidence is not tempered.
Analysis
In this stage, the investigator refreshes the defined data and concludes the available evidence. However, it could take several rounds of analysis to support a certain crime scenario.
Documentation
A record of all the data that is readily visible must be make during this phase. It helps to refresh and identify crime scenes and review them. It involves proper crime scene documentation, including photos, sketches, and crime-scene mapping.
Presentation
The process of summarizing and explaining the conclusion is completed in this final phase. However, it should be stated using simplified terminologies and in layman’s words. Every abstract terminology must be refer to as special.
Types of Digital Forensics
There are different types of digital forensic.
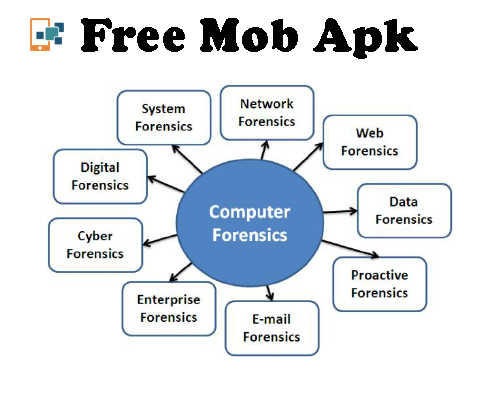
Disk Forensics:
It scans for active, modified, or deleted files and processes data extracted from the storage media.
Network Forensic:
It is a sub-branch of Digital forensics. It is related to monitoring and analyzing computer network traffic to collect sensitive information and forensic evidence.
Wireless Forensics:
It is a division of network forensics. The main objective of wireless forensics is to provide the necessary tools to collect and analyze traffic data for wireless networks.
Database Forensics:
It is a branch of digital forensics that deals with studying and examining databases and their related metadata.
Malware Forensic:
This branch handles identifying malicious code, studying their payload, viruses, worms, and more.
Email Forensics:
It includes recovery and analysis of deleted emails, calendars, contacts, etc.
Memory Forensics:
It involves collecting raw format data from system memory (system registers, cache, RAM) and removing data from raw dumps.
Mobile Phone Forensics:
It mainly describes the testing and analysis of mobile devices. It helps you find phone and SIM card contacts, call history, incoming and outgoing SMS / MMS, audio, video, and more.
Challenges Faced by Digital Forensics
Here are the main challenges of digital forensic are:
- The rapid growth of personal computers and the extensive use of Internet access
- Easy availability of the hacking tool
- Due to the lack of physical evidence, it is hard to bring proceedings
- A large amount of disk space in terabytes complicates this testing task
- Any technical development requires an update or modification of the solution
What Kind of Jobs Can You Get in Digital Forensics?
Most digital forensics professionals’ jobs can find in the public sector. Apart from the apparent position in law enforcement and government agencies, there are also jobs in the private sector, such as I.T. companies, public institutions, and financial institutions. Experts in this field have two important roles. They prevent possible cybercrime, ensure cyber security or participate in the investigation of crimes already committed. There are a variety of digital facts roles to choose from depending on education, skills, experience, and seniority.
Computer Forensics Investigator
Digital Forensic Investigator
Computer Expertise Technician
Information Security Analyst
Digital Forensics Analyst
Digital/Computer Forensic Engineer
Information Systems Security Analyst
Computer Forensics Analyst
Cyber Security Consultant
Computer / Digital Forensic Technician
In the current circumstances, a career in the field of digital forensics has good prospects. Search engines for jobs like Glassdoor, PayScale, and the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics offer impressive salary projections for digital forensic jobs. According to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics, demand for this field will increase.
Example Uses of Digital Forensics
More recently, commercial organizations are using digital forensic to track these cases.
- Intellectual property theft
- Industrial espionage
- Employment disputes
- Fraud investigations
- Internet and Email abuse in the workplace
- Forgeries related matters
- Bankruptcy investigations
- Issues concerned with the regulatory compliance
- Purpose Digital Forensics
The most common use of digital forensics is to support or disprove hypotheses in criminal or civil courts.
Criminal Cases: Includes alleged violations of the law and law enforcement agencies and digital forensics investigators.
Civil Cases: Includes protection of rights and property of individuals or contractual disputes between commercial enterprises where a form of digital forensics called electronic discovery (eDiscovery).
Advantages
Here are the major Pros/Advantages of using digital forensic are:
To protect the computer system’s integrity
To present evidence in court that will allow the culprit to be punished
It helps the companies to collect critical information if their computer system or networks are compromised.
Successfully locate cyber criminals wherever in the world
It helps to protect your company’s valuable time and money.
Allows extracting, process, and interpreting factual evidence, proving the cybercriminal action’s in court.
Disadvantages
Here is major cons/disadvantages of using digital forensic are:
Digital evidence has been submitted to the court. However, it must be proved that there is no tempering.
Creating and storing electronic records is very expensive.
Legal practitioners should have extensive computer knowledge.
Need to produce authentic and convincing evidence
Courts may not accept evidence if digital forensic equipment does not meet specific criteria.
The investigation officer’s lack of technical knowledge will not yield the expected results.
Read Also>>>>What is Wireless Technology
Conclusion
Digital forensics is a generic term for computer forensics. Now it is an applied discipline focused on solving computer crimes, investigating digital evidence, and methods of finding, recovering, and securing that evidence. Digital forensic deals with all data that appears on digital devices.
Digital forensics, also known as computer forensics or cyber forensics is the practice of legally collecting, processing, analyzing, and preserving digital evidence for cybercrimes. This includes the presentation of such evidence in civil or criminal courts. Digital Forensic is often to use in court cases or criminal investigations by private sector organizations to protect data and identify criminal activity.

